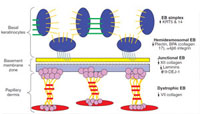
What structural components of the epidermis are involved in blistering diseases? | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Fig. 1.4 This diagram of the dermal epidermal junction illustrates the affected levels in the various types of epidermolysis bullosa (EB). |
| Table 1-1. Diseases Associated with Antibodies and Damage to Desmosomes | |||||
| DISEASE INVOLVED | CLINICAL APPEARANCE AND LOCATION | MAIN DERMOSOMAL MOLECULES | |||
Pemphigus vulgaris | Oral and diffuse superficial flaccid blisters with ulcers | Desmogleins 1 and 3 (Dsg1 and 3) and plakoglobin | |||
Pemphigus foliaceus | Diffuse superficial blisters and crusting | Desmoglein 1 (Dsg1) | |||
Pemphigus vegetans | Vegetating, weeping lesions in the intertriginous areas | Desmoglein 3 (Dsg3) | |||
Pemphigus erythematosus | Butterfly eruption with blistering in malar areas | Desmoglein 3 (Dsg3) | |||
Paraneoplastic pemphigus | Diffuse erythema multiforme-like painful eruption | Desmoplakins 1 and 2 (Dsg1 and 2), BP antigen 1 (BP230), plectin, desmogleins 1 and 3 (Dsg1 and 3), envoplakin, periplakin | |||
IgA pemphigus | Pustular or vesiculopustular eruption | Desmogleins 1 and 3 (Dsg1 and 3), desmocollin 1 | |||
© 2025 Skin Disease & Care | All Rights Reserved.